Science
Our Clinical Candidate
Mocravimod (KRP-203) is a modulator of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors given during and after the stem cell transplant procedure and it has shown promising initial clinical results in rebalancing the immune system.
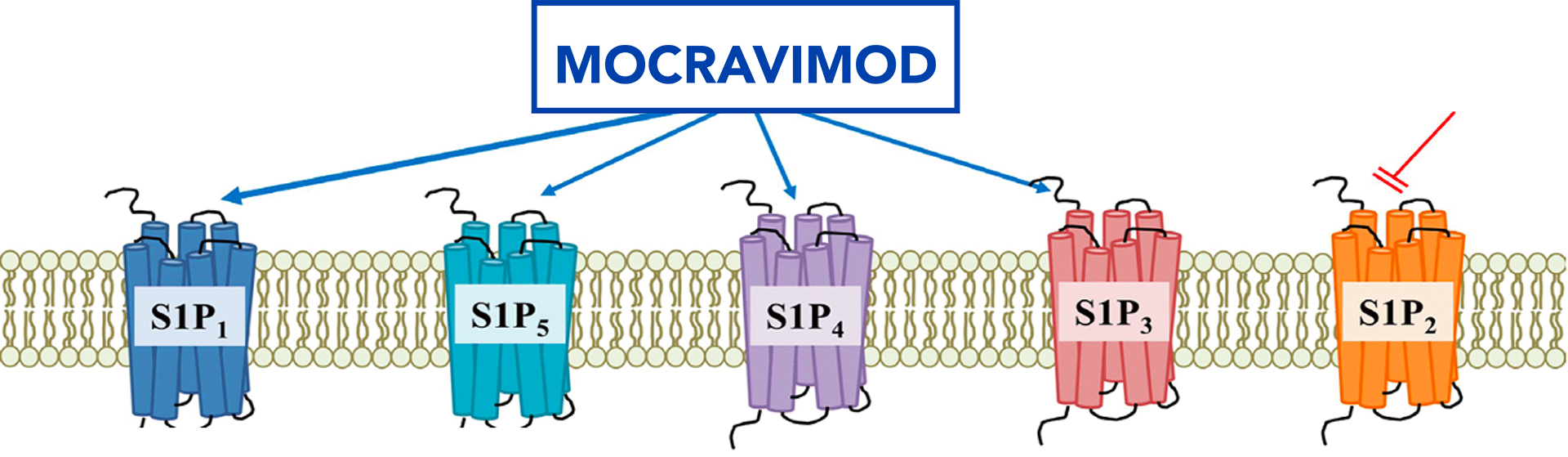
Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT)
HCT provides donor stem cells to reach the bone marrow engraft and repopulate the immune system. At the same time, by adding mocravimod, the donor-derived alloreactive T cells are sequestered in lymph nodes and other secondary lymphoid organs.
By the sequestration process two positive effects are triggered:
- GvHD is reduced because the alloreactive T cells do not migrate into peripheral tissues
- The alloreactive T cells in the lymph nodes and the white pulp of the spleen have a killing effect of the remaining malignant hematopoietic cells that escaped from the chemotherapy

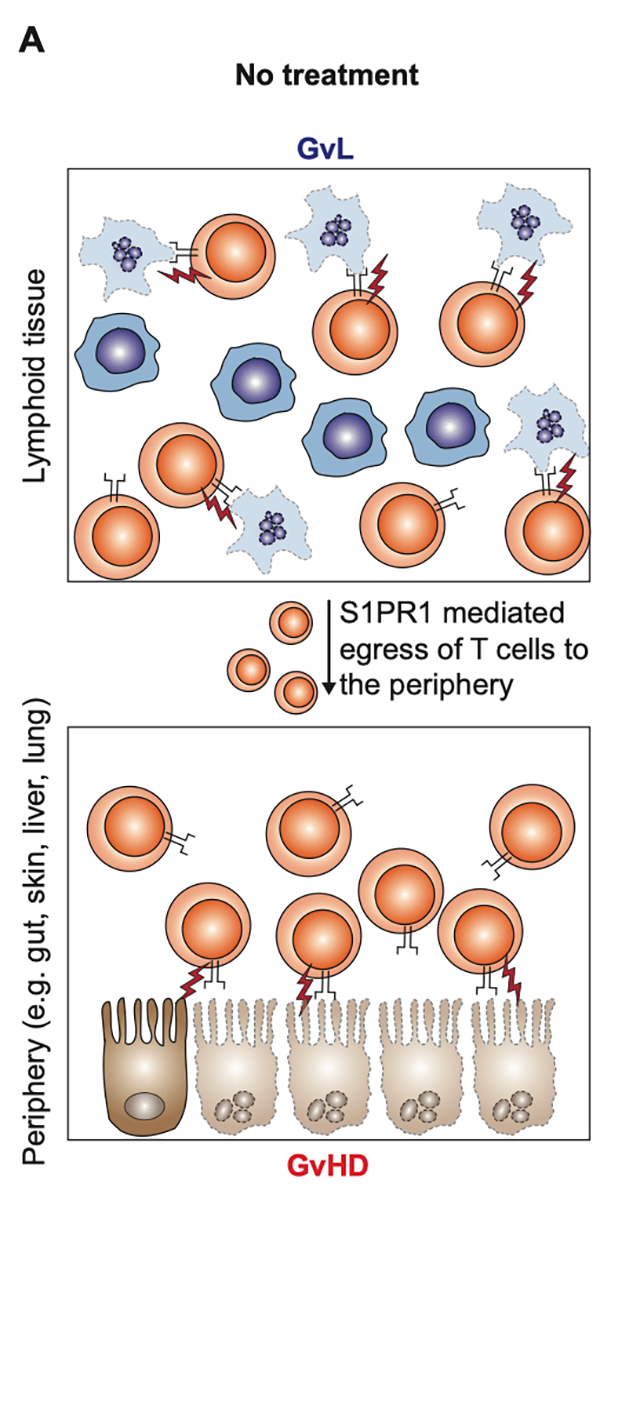
Following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), alloreactive donor T cells migrate to lymph nodes where they are activated and proliferate. Activated donor T cells are capable of killing leukemic cells through a process called graft-versus-leukemia (GvL) reaction. Alloreactive donor T cells express S1PR1 on their surface, and signaling through this receptor allows for their egress from the lymph node to peripheral tissues, such as the gut, skin, liver and lung. Through allo-recognition of their target tissue, donor T cells cause inflammation and tissue damage resulting in graft-versus-host disease (GvHD).
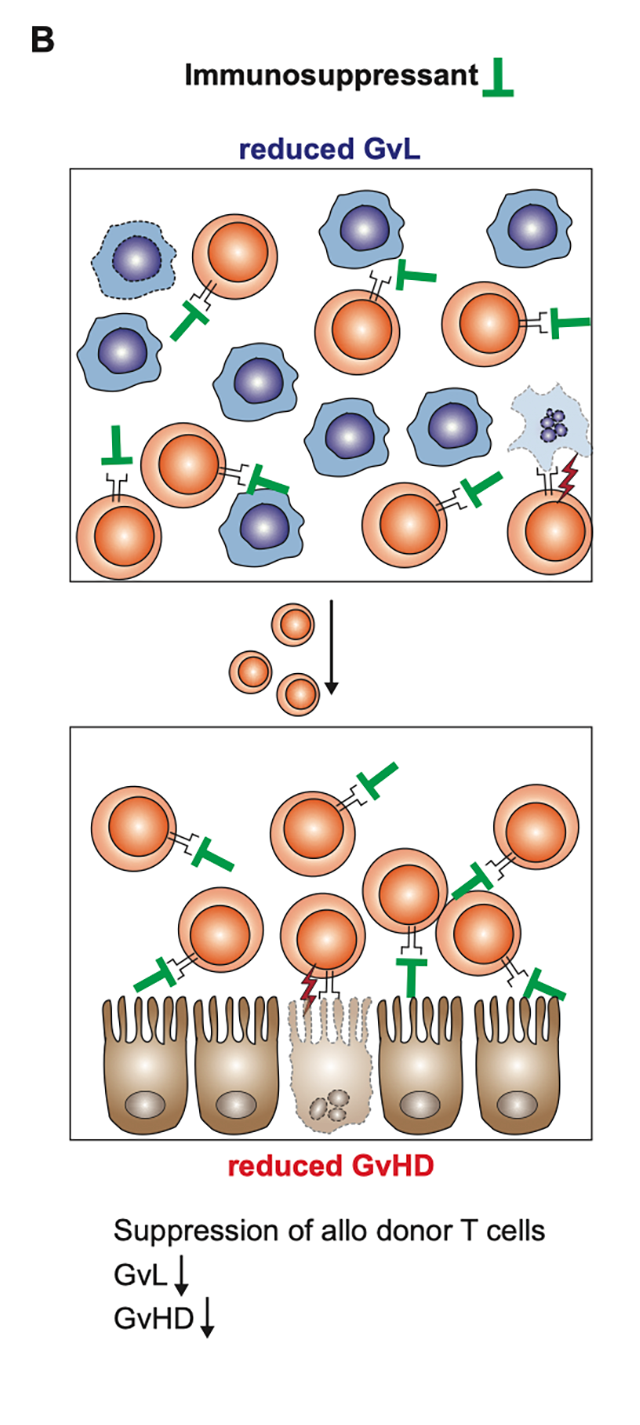
Immunosuppressive drugs are used for the prevention and treatment of GvHD. However, T cell suppression is non-specific and as a consequence the beneficial GvL reaction is suppressed, too. Reduced GvL bears the risk of increased relapse and limits the successful outcome of allogeneic HCT. In conclusion, GvHD is suppressed at the expense of also suppressing GvL.
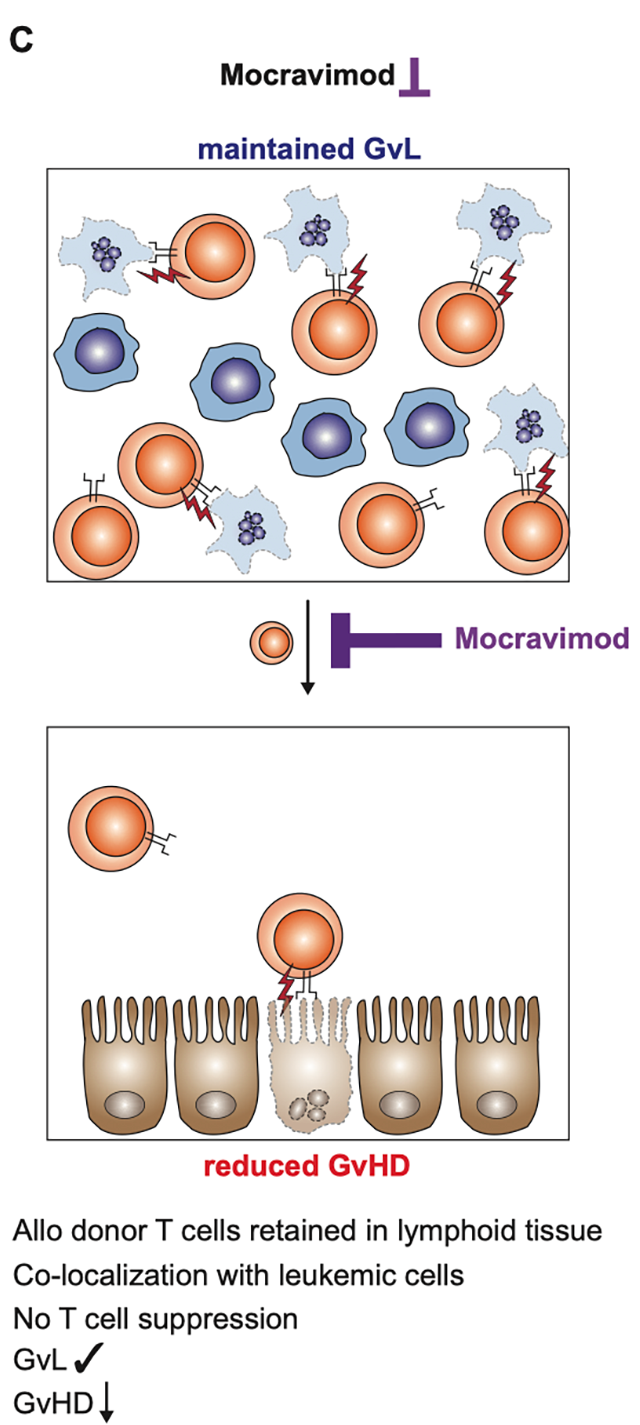
Mocravimod, a pharmacological modulator of S1PR signaling, blocks the signal required by T cells to egress from the lymph node to the periphery. Consequently, fewer alloreactive donor T cells migrate to peripheral tissues, resulting in reduced GvHD-caused tissue damage. However, the beneficial GvL effect is maintained, thus leukemic cells remain efficiently killed. In conclusion, GvL is maintained while GvHD is suppressed.
The impact of acute Myeloid Leukemia
New estimated cases of leukemia (all kinds) in the US in 2020
New estimated cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the US in 2020
Estimated deaths from AML in the US in 2020
*From the American Cancer Society – Estimates for leukemia in the US for 2020
Our Pipeline
We are investing heavily in clinical activities and intellectual property management. We have one clinical-stage therapeutic candidate, mocravimod, that is ready to enter the registration-enabling phase II/III study. Mocravimod was tested positively in extensive Phase I, Phase 2a autoimmune clinical studies (Ulcerative Colitis, scLE, Crohn’s Disease) and in Phase 2a Hematological Malignancies HCT clinical studies.

